

Value stream mapping helps an organization identify the non-value-adding elements in a targeted process. Value Stream Mapping. This technique involves flowcharting the steps, activities, material flows, communications, and other process elements that are involved with a process or transformation (e.g., transformation of raw materials into a finished product, completion of an administrative process).There was no strainer attached, and metal scrap got in. The shaft of the pump was worn and rattling. The lubrication pump was not pumping sufficiently. Why was it not lubricated sufficiently?.The bearing was not sufficiently lubricated. There was an overload, and the fuse blew. Five Whys. Toyota developed the practice of asking "why" five times and answering it each time to uncover the root cause of a problem.Two techniques are commonly used to define the current state and identify manufacturing wastes: Phase 2: Implementation. The team first works to develop a clear understanding of the "current state" of the targeted process so that all team members have a similar understanding of the problem they are working to solve. Team members are expected to shed most of their operational responsibilities during this period, so that they can focus on the kaizen event.
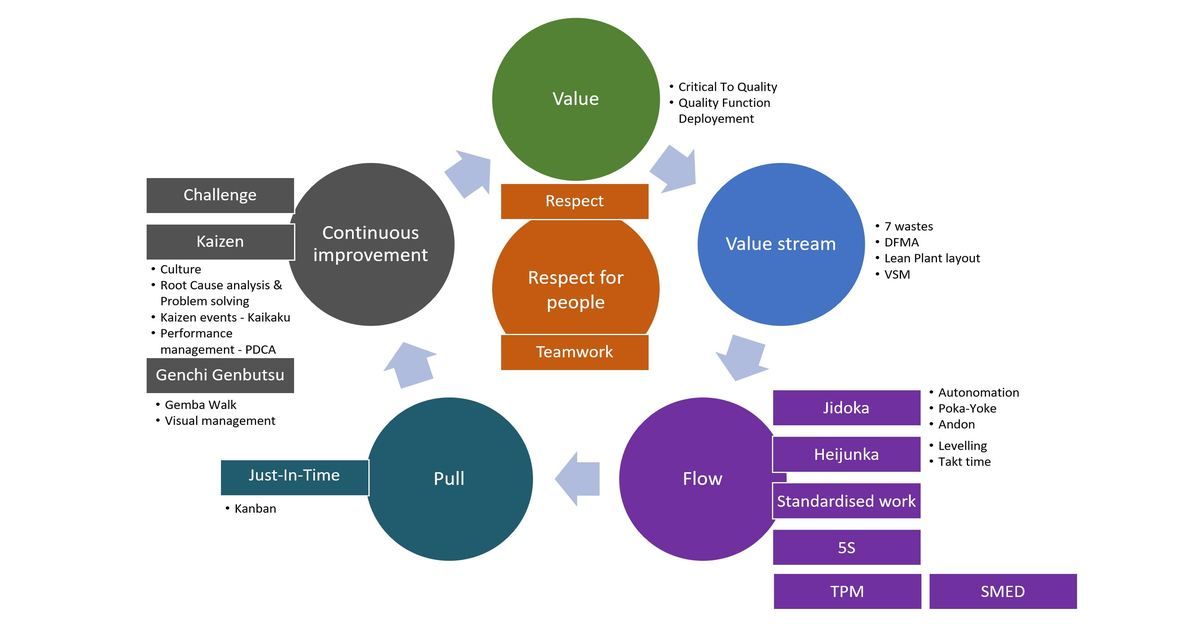
Kaizen events are generally organized to last between one day and seven days, depending on the scale of the targeted process and problem. Team members should all be familiar with the organization's rapid improvement process or receive training on it prior to the "event". It is important for teams to involve workers from the targeted administrative or production process area, although individuals with "fresh perspectives" may sometimes supplement the team. Once the problem area is chosen, managers typically assemble a cross-functional team of employees. Once a suitable production process, administrative process, or area in a factory is selected, a more specific "waste elimination" problem within that area is chosen for the focus of the kaizen event ( i.e., the specific problem that needs improvement, such as lead time reduction, quality improvement, or production yield improvement). Such areas might include: areas with substantial work-in-progress an administrative process or production area where significant bottlenecks or delays occur areas where everything is a "mess" and/or quality or performance does not meet customer expectations and/or areas that have significant market or financial impact (i.e., the most "value added" activities). Phase 1: Planning and Preparation. The first challenge is to identify an appropriate target area for a rapid improvement event. The basic steps for implementing a kaizen "event" are outlined below, although organizations typically adapt and sequence these activities to work effectively in their unique circumstances. Most organizations implementing kaizen-type improvement processes have established methods and ground rules that are well communicated in the organization and reinforced through training. Rapid continual improvement processes typically require an organization to foster a culture where employees are empowered to identify and solve problems.

Top of Page Method and Implementation Approach Kaizen can be used as an analytical method for implementing several other lean methods, including conversions to cellular manufacturing and just-in-time production systems. Periodic follow-up events aim to ensure that the improvements from the kaizen "blitz" are sustained over time. The team works to implement chosen improvements rapidly (often within 72 hours of initiating the kaizen event), typically focusing on solutions that do not involve large capital outlays. The team uses analytical techniques, such as value stream mapping and "the 5 whys", to identify opportunities quickly to eliminate waste in a targeted process or production area. The kaizen strategy aims to involve workers from multiple functions and levels in the organization in working together to address a problem or improve a process. This philosophy implies that small, incremental changes routinely applied and sustained over a long period result in significant improvements. Lean production is founded on the idea of kaizen – or continual improvement. Kaizen focuses on eliminating waste, improving productivity, and achieving sustained continual improvement in targeted activities and processes of an organization. Kaizen, or rapid improvement processes, often is considered to be the "building block" of all lean production methods.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
